Depth of Earthquakes at Convergent Boundaries
It has a length of about 40000 kilometers. Earthquake belts and distribution.
11 2 Earthquakes And Plate Tectonics Physical Geology
In summary convergent boundaries generate earthquakes because like any other plate boundary the plates involved in this boundary can lock putting enormous stresses on the boundary.
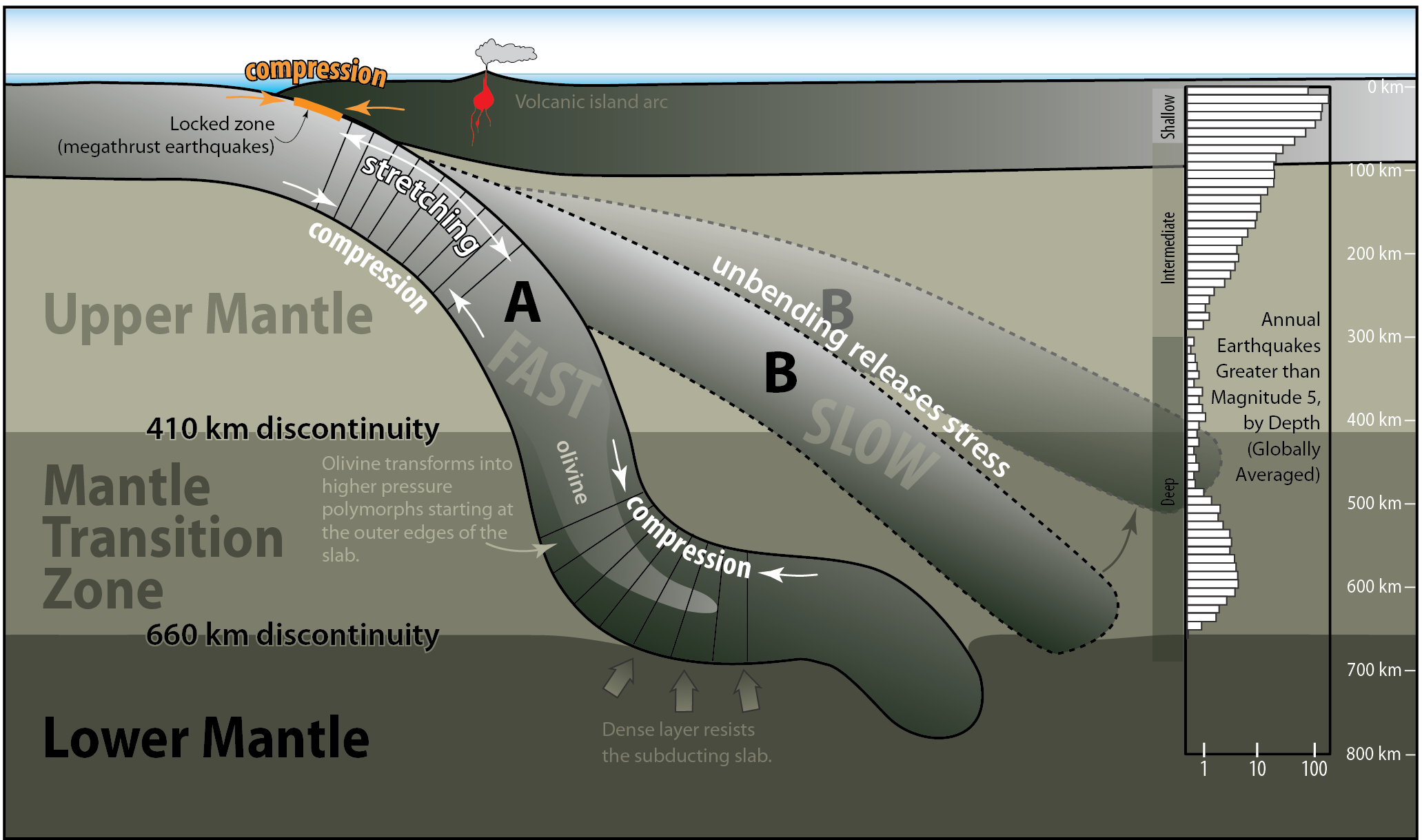
. This is an earthquake. The frequency of earthquakes is greatest near the surface and especially around the area where large subduction quakes happen but it extends to at least a 400 kilometre depth. Earthquakes occur in welldefined belts that correspond to active plate tectonic zones.
They occur almost exclusively at convergent boundaries in association with subducted oceanic lithosphere. The frequency of earthquakes is greatest near the surface and especially around the area where large subduction quakes happen but it extends to at least 400 km depth. There are two different types of convergent margins that have different types of earthquakes associated with them.
While deep quakes may be less dangerous they tend to be felt by more people explains the USGS. Along convergent plate margins with subduction zones earthquakes range from shallow to depths of up to 700 km. 70 to 300 kilometers depth blue.
How earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries. When convergence of continent and ocean occurs the ocean plate is subducted beow. The deepest earthquake ever recorded was a small 42 earthquake in Vanuatu at a depth of 7358 km in 2004.
Up to 24 cash back Convergent Boundaries happen when one tectonic plate is sliding under the adjacent tectonic plate. Click to see full answer. As the plates move past each other they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up.
Earthquakes occur where the two plates are in contact as well as in zones of deformation on the overriding plate and along the subducting slab deeper within the mantle. In order for an earthquake to occur two blocks of crust must slip past one another and it is impossible for this to happen at or above the surface of the earth. The circumPacific belt also called the Rim of Fire follows the rim of the Pacific Ocean and hosts over 80 percent of the worlds shallow and mediumdepth earthquakes and 100 percent of the deep earthquakes.
India plate and Eurasian plate featuring the Himalayas This boundary is a continent-continent convergent boundary. 0-50 km 51-100 km 101-200 km 201-400 km This question uses Geotours Workbook B. Its boundaries border other plates such s the Philippine North American Nazca Indian-Australian Cocos Juan de Fuca and Pacific plates.
Below this depth the crust is hot enough that it no longer behaves in a brittle way. Convergent Boundary - Nazca Trench. Subduction zone convergent boundaries Explnation.
Convergent boundaries are where two plates come together. Earthquakes at Convergent Boundaries Subduction Zones Along convergent plate margins with subduction zones earthquakes range from shallow to depths of up to 700 km. Earthquakes at convergent plate boundaries are distributed with predictable locations and depths.
0 to 33 kilometers depth orange. Are deep focus earthquakes more dangerous. Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundariesdivergent convergent and transform.
As the two plates collide one plate is forced down underneath the other. Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. Earthquakes occur where the two plates are in contact as well as in zones of deformation on the overriding plate and along the subducting slab deeper within the mantle.
The depth of earthquake in zone 1. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure energy is released as seismic waves causing the ground to shake. 33 to 70 kilometers depth green.
An earthquake cannot physically occur at a depth of 0 km or -1km above the surface of the earth. 300 to 700 kilometers depth Spreading ridges are heavy lines subduction zones are toothed lines and transform faults are light lines. Where do earthquakes occur at convergent boundaries.
A deep-focus earthquake in seismology also called a plutonic earthquake is an earthquake with a hypocenter depth exceeding 300 km. In subduction zones where older and colder oceanic crust sinks under another tectonic plate deep-focus earthquakes may. Most of deep-focus earthquakes occur at oceanic convergent boundaries.
Distribution of earthquakes of M4 and greater in the Central America region from 1990 to 1996 red. The plate that is the most dense will subduct beneath the other plate see the image below creating uplift mountain building or plates with comparable densities will mash into each other creating uplift even though there is still going to be at least some subductionGenerally speaking the older of the. Along convergent plate margins with subduction zones earthquakes range from shallow to depths of up to 700 km.
Eventually the boundary cant take the stress and it ruptures generating an earthquake. Check and double-click the Problem 11 placemark to fly to South America. Earthquakes occur where the two plates are in contact as well as in zones of deformation on the overriding plate and along.
The diagram to the left is an example of an oceanic crust moving under a continental crust. Most large tsunamis occur at convergent plate boundaries where two tectonic plates are crashing into each other. Deep large magnitude earthquakes commonly occur at convergent plate boundaries.
The background seismicity at this convergent boundary and on other similar ones is predominantly near the upper side of the subducting plate. Earthquakes occurring at a depth of less than 70 km 43 mi are classified as shallow-focus earthquakes while those with a focal depth between 70 km 43 mi and 300 km 190 mi are commonly termed mid-focus or intermediate-depth earthquakes. Do convergent boundaries cause tsunamis.
What is the depth of the majority of earthquakes directly beneath the volcanic arc associated with this subduction zone. We have a new and improved read on this topic. This movement causes upheavals of the plate that is on top as well as creating a trench along the boundaries of the two plates as they move into each other.
Range from shallow to deep These earthquakes are associated with. Higher Order Thinking Skills Goals. How and why convergent plate boundaries cause massive earthquakes.
Also 90 of all earthquakes take place here. These earthquakes occur at greater depths ranging from 300 km to 700 km in the Earths subsurface. Earthquakes occur down to a maximum depth of about 600 km.

12 3 Earthquakes And Plate Tectonics Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition

Map Of Shallow Depth Earthquakes In The Region Of This Study With Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "Depth of Earthquakes at Convergent Boundaries"
Post a Comment